As digital technology advances, online security methods are evolving too. CAPTCHAs, which help confirm that a user is human, have become a standard tool to stop bots from exploiting web services. Frequently, we encounter these tests and simply check the “I am not a robot” box. However, what implications does this simple action carry?
CAPTCHAs play an essential role in protecting websites from automated programs that can overwhelm servers, capture sensitive information, or commit fraud. By confirming they are not robots, users contribute to a system aimed at ensuring online safety and security. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of these measures is frequently debated.
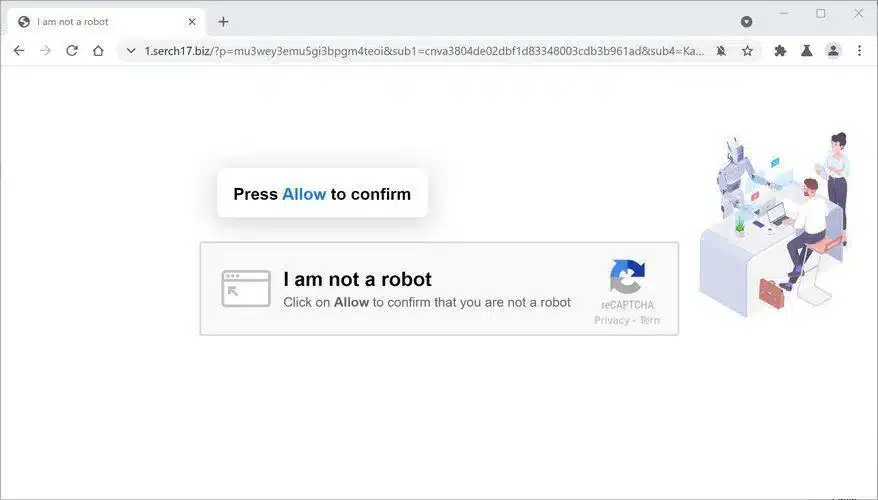
Over the years, CAPTCHA technology has progressed remarkably. Originally, these tests featured distorted text that posed challenges for bots yet were decipherable by humans. Nowadays, we face different CAPTCHA formats, such as image recognition tasks, where users are required to identify particular objects among a set of images.
Although the purpose of CAPTCHAs is commendable, they can occasionally disrupt the user experience. Numerous users express frustration when they struggle to pass a CAPTCHA despite multiple tries. This prompts a critical question: are these verification systems ultimately causing more issues than they solve?

Additionally, there are accessibility concerns. Individuals with disabilities may struggle to complete specific types of CAPTCHAs, thereby restricting their access to services that depend on these verification tools. As the internet strives for inclusivity, it’s vital to examine how CAPTCHAs affect every user.

With ongoing technological advancements, developers are striving to create verification methods that enhance user experience while preserving security. Innovations such as biometric authentication and behavioral analysis may eventually supplant traditional CAPTCHAs, leading to a more seamless online experience for all users.
